Saturday, May 23, 2015
Sailor's Delight
Games Reviewer
8:11 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logic puzzles
,
logical games
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
sailor
,
web puzzles
No comments
:
10 pirates are ranked in order, first to last. After finding a
treasure chest of 100 gold coins, they are discussing how to divide up
the booty. They allow the lowest ranked sailor to divide up the coins
and then vote on his idea. If the number of pirates who like the
division is equal to or greater than the others who don't like it, then
the boss will say, "Make it So." (The proposer of the idea also has a
vote.)
Otherwise... well, being pirates their simple solution is to dump the unfortunate sailor into the deep blue sea and let the next pirate in line decide how to divide up the spoils.

How many pirates will be thrown into the sea?
Otherwise... well, being pirates their simple solution is to dump the unfortunate sailor into the deep blue sea and let the next pirate in line decide how to divide up the spoils.

How many pirates will be thrown into the sea?
Notes:
- Pirates are smart, want money, and love life, especially their own!
- This one is harder than average. If you are stuck, think of fewer pirates...
- Why would #1 ever vote for any schemes?
- Why would #2 ever vote for any schemes?
- ... hmmmm
Sailor's Delight Puzzle Solution
We asked you readers to send us a solution to this puzzle, and we kept an open mind about it.The first person with a simple, elegant, and, in our opinion, valid solution, is Saurabh Gupta, a faithful reader and avid puzzler. Here is Saurabh's solution.
How many pirates will be thrown into the sea? None. And the correct distribution is:
| Pirate with rank |
Number of coins |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 |
| 6 | 1 |
| 7 | 0 |
| 8 | 1 |
| 9 | 0 |
| 10 | 96 |
Pirate 10 divided the coins. He will get the votes of pirates 2, 4, 6, 8, and himself. This is taking into consideration what each of the pirates will get if this plan is not passed.
Starting with a situation when there is only pirate 1. He keeps all the 100 coins for himself and live happily by passing the division with his only vote.
In case that there are two pirates, pirate 2 divides and he keeps 100 coins for himself while giving none to pirate 1. He still gets the division passed with his vote and live happily ever after.
In case there are three pirates, pirate 3 divides and gives pirate 1 a single coin and keeps the other 99 coins for himself. Pirate 1 would now vote in his favor because if he votes against, then pirate 2 would get a chance to divide and would keep all the loot for himself.
If four pirates are present, pirate 4 divides and now gives pirate 2 a single coin to gain his vote (who otherwise gets nothing if pirate 3 has a chance to divide the coins). In this case, pirates 1 and 3 get nothing.
Therefore, in a similar manner, the distribution when there is an extra pirate is achieved as follows:
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There is, however, still some doubt about this solution. After all, it was said that pirates are smart. With this solution, based on a method of dividing the booty supposedly approved by all, it is shown that only one (the last one) is very smart, while 4 of them get only a coin, and 5 of them get nothing. This seems to be in conflict with the statement that pirates are smart. Even if the method was approved only by half of them (the ones who get at least a coin), 4 of these voters don't seem very smart if they get only one coin. Certainly, it couldn't have been a dictatorship decision taken by the leader, as he ends up empty-handed.
An alternative, to make the pirates look brighter, is that the dividing pirate actually shares the loot evenly between the pirates likely to give him a positive vote. In that case, the pirates who previously got only one coin, end up getting just as much as the lowest ranked, while the others get nothing again. This would entail the following solution:
| Pirate with rank |
Number of coins |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 20 |
| 3 | 0 |
| 4 | 20 |
| 5 | 0 |
| 6 | 20 |
| 7 | 0 |
| 8 | 20 |
| 9 | 0 |
| 10 | 20 |
This alternative solution, however, defies a bit the mechanism of the division logic and process explained in the main solution. Perhaps, it would be fair to make a re-wording of the puzzle, stating that, although pirates are smart, the method of dividing the booty is forced on them by some external entity, and no pirate, not even the leader, can oppose to it. However, a rewording of the puzzle will NOT take place, as this is how it was presented on Brent's page, and we are going to preserve it.
Also, it might be possible that this is not the only acceptable solution, and another alternative solution might exist, that doesn't raise any doubts with the puzzle premises.
So, we are still asking you: send us your solution!
Monday, May 18, 2015
12 Balls
Games Reviewer
8:09 AM
balls
,
balls puzzle
,
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
play puzzle games
,
puzzle
,
stimulate brain activity
No comments
:
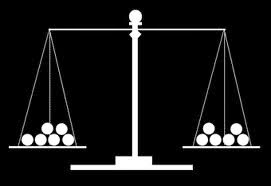
You have twelve balls that all weigh the same except one, which is either slightly lighter or slightly heavier. The only tool you have is a balance scale that can only tell you which side is heavier.
Using only three weighings, how can you deduce, without a shadow of a doubt, which is the odd one out, and if it is heavier or lighter than the others?
12 Balls Puzzle Solution
We found a good solution to this puzzle on the Cut The Knot website. They show a solution taken from the book Mathematical Spectrum, by Brian D. Bundy. Bundy shows two solutions: the first one requires different courses of action depending on the outcome of previous weighings, so it is not particularly elegant or easy to remember. The second solution involves a fixed course of action in all circumstances, and is the one that follows.In this method we weigh four specified balls against four other specified balls in each of the three weighings and note the result. If we observe say the left hand side of the balance, then for an individual weighing there are three possible alternatives: the left hand side is heavy (>), light (<) or equal (=) as compared with the right hand side of the balance.
Since three weighings are allowed, the number of different results that can be obtained is just the number of arrangements (with repetitions allowed) of the three symbols >, <, =, i.e. 3 3 = 27. If we use all twelve balls in the three weighings, and ensure that no particular ball appears on the same side of the balance in all three weighings, the outcomes >>>, <<<, === are not possible. We thus have only 24 possible outcomes and we shall show that it is possible to set up a one to one correspondence between these 24 outcomes and the conclusion that a particular ball among the twelve is heavy or light.
The 24 outcomes can be divided into two groups of twelve in each group. If we call the reverse of an outcome the outcome obtained by replacing > by <, < by > and leaving = unchanged, one group of twelve will be the reverses of the other group and vice versa. We can thus write the 24 outcomes in the form of two arrays, each array having three rows (the three weighings) and twelve columns (the twelve balls), so that each row contains four >'s, four <'s and four ='s. Thus we have, for example,
< = = = < < > > > < > =
= > < = > = < > > = < <
A B C D E F G H I J K L
< < < < > > > > = = = =
> = = = > > < < < > < =
= < > = < = > < < = > >
Wednesday, May 13, 2015
Hugh's Horses
Games Reviewer
8:07 AM
brain
,
horses
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
riddle online
No comments
:
A horse breeder goes to a horse show with a certain number of horses.
The first buyer comes by and purchases half of the horses the breeder
brought plus half a horse. The second buyer comes by and purchases half
of what remains plus half a horse. The third buyer comes by and
purchases half of what remains plus half a horse. The breeder leaves,
satisfied that he has sold all the horses he brought.
All three buyers have purchased whole horses, and there is no shared ownership among them.
How many horses did the breeder bring to the show?
All three buyers have purchased whole horses, and there is no shared ownership among them.
How many horses did the breeder bring to the show?
Hugh's Horses Puzzle Solution
(0.5 + 0.5) + (0.5 + 1.5) + (0.5 + 3.5) = 7.Or here's a an algebraic solution kindy submitted by Greg Bradshaw. Thanks!
Solve for x where x is the total number of horses:
x = (.5x + .5) + (.5(.5x - .5) + .5) + (.5[.5{.5x - .5} - .5] + .5)
x = .5x + .5 + .25x - .25 + .5 + .5(.25x - .25 -.5) + .5
x = .5x + .5 + .25x + .25 + .5(.25x - .75) + .5
x = .5x + .5 + .25x + .25 + .125x - .375 + .5
x = .5x + .5 + .25x + .25 + .125x + .125
x = .875x + .875
.125x = .875
x = .875/.125
x = 7
Friday, May 8, 2015
The Dog Situation
Games Reviewer
8:05 AM
brain
,
dog
,
dog situation puzzle
,
logic
,
logical games
,
play puzzle games online
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
No comments
:

Of the eight dogs, three are cocker spaniels, three are terriers, and two are dachshunds. None of the four boys owns two dogs of the same breed. No two dogs of the same breed have the same name. Neither of Alec's dogs is named David and neither of Charlie's dogs is named Alec. No cocker spaniel is named Alec, and no terrier is named David. Bob does not own a terrier.
What are the names of the dachshunds, and who are their owners?
The Dog Situation Puzzle Solution
One of the dachshunds is owned by Bob and is named Alec, while the other is owned by Charlie and is called David.To get to the solution, let's gather all the information we're given:
1 Each boy has named his dogs after two of his brothers
2 Each boy has two doggy namesakes
3 There are 3 cocker spaniels, 3 terriers, and 2 dachshunds
4 None of the four boys owns two dogs of the same breed
5 No two dogs of the same breed have the same name
6 Neither of Alec's dogs is named David
7 Neither of Charlie's dogs is named Alec
8 No cocker spaniel is named Alec
9 No terrier is named David
10 Bob does not own a terrier
With this info, it follows that:
11 Alec's dogs are named Bob and Charlie (from 6 and 1)
12 Charlie's dogs are named Bob and David (from 7 and 1)
13 David's dogs are named Alec and Charlie (from 11, 12, 1 and 2)
14 Bob's dogs are named Alec and David (from 11, 12, 13, 1 and 2)
15 Bob's dogs are a cocker and a dachshund (from 3, 4 and 10)
16 The 3 cockers are called Bob, Charlie, and David (from 3, 5 and 8)
17 The 3 terriers are called Alec, Bob, and Charlie (from 3, 5 and 9)
18 The 2 dachshunds are called Alec and David, because the names Bob and Charlie are already taken by cockers and terriers (from 2, 3, 16 and 17)
19 Bob's dachshund must be called Alec, because there are no cockers with that name (from 14, 15, 16 and 18)
20 Bob's cocker is called David (from 14, 15, 16, 18 and 19)
21 The dachshund called David must belong to Charlie (from 12, 18 and 20)
Deductions 19 and 21 have given us the solution to the puzzle.
Sunday, May 3, 2015
Who Owns The Zebra?
Games Reviewer
8:03 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzles
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
zebra
,
zebra puzzle
No comments
:
There are five houses.
Each house has its own unique color.
All house owners are of different nationalities.
They all have different pets.
They all drink different drinks.
They all smoke different cigarettes.
The English man lives in the red house.
The Swede has a dog.
The Dane drinks tea.
The green house is on the left side of the white house.
They drink coffee in the green house.
The man who smokes Pall Mall has birds.
In the yellow house they smoke Dunhill.
In the middle house they drink milk.
The Norwegian lives in the first house.
The man who smokes Blend lives in the house next to the house with cats.
In the house next to the house where they have a horse, they smoke Dunhill.
The man who smokes Blue Master drinks beer.
The German smokes Prince.
The Norwegian lives next to the blue house.
They drink water in the house next to the house where they smoke Blend.
So, who owns the Zebra?

Each house has its own unique color.
All house owners are of different nationalities.
They all have different pets.
They all drink different drinks.
They all smoke different cigarettes.
The English man lives in the red house.
The Swede has a dog.
The Dane drinks tea.
The green house is on the left side of the white house.
They drink coffee in the green house.
The man who smokes Pall Mall has birds.
In the yellow house they smoke Dunhill.
In the middle house they drink milk.
The Norwegian lives in the first house.
The man who smokes Blend lives in the house next to the house with cats.
In the house next to the house where they have a horse, they smoke Dunhill.
The man who smokes Blue Master drinks beer.
The German smokes Prince.
The Norwegian lives next to the blue house.
They drink water in the house next to the house where they smoke Blend.
So, who owns the Zebra?

Who Owns The Zebra? Puzzle Solution
The German owns the zebra!| #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationality | Norwegian | Dane | English | German | Swede |
| Colour | Yellow | Blue | Red | Green | White |
| Drink | Water | Tea | Milk | Coffee | Beer |
| Cigarettes | Dunhill | Blend | Pall Mall | Prince | Blue Master |
| Pets | Cats | Horse | Birds | Zebra | Dog |
Tuesday, April 28, 2015
Socks And Shops
Games Reviewer
8:01 AM
brain
,
brain teasers
,
games online
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzle
,
puzzle
,
puzzles online
,
shops
,
socks
No comments
:

Without being able to see the colour of the socks, how could they divide them so that they both got 10 pairs of uniquely coloured socks each?
Socks And Shops Puzzle Solution
For each of the twenty pairs of socks, they unclipped it and gave one sock each.Thursday, April 23, 2015
Strawberry Ice Cream
Games Reviewer
8:00 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzles
,
play puzzle games
,
puzzle
,
puzzles online
,
riddles online
,
strawberry ice cream
No comments
:
A man walks into a bar, orders a drink, and starts chatting with the bartender.
After a while, he learns that the bartender has three children. "How old are your children?" he asks.
"Well," replies the bartender, "The product of their ages is 72."
The man thinks for a moment and then says, "That's not enough information."
"All right," continues the bartender. "If you go outside and look at the building number posted over the door to the bar, you'll see the sum of the ages."
The man steps outside, and after a few moments he reenters and declares, "Still not enough!"
The bartender smiles and says, "My youngest just loves strawberry ice cream."
How old are the children?
After a while, he learns that the bartender has three children. "How old are your children?" he asks.
"Well," replies the bartender, "The product of their ages is 72."
The man thinks for a moment and then says, "That's not enough information."
"All right," continues the bartender. "If you go outside and look at the building number posted over the door to the bar, you'll see the sum of the ages."
The man steps outside, and after a few moments he reenters and declares, "Still not enough!"
The bartender smiles and says, "My youngest just loves strawberry ice cream."

How old are the children?
Strawberry Ice Cream Puzzle Solution
First, determine all the ways that three ages can multiply together to get 72:- 72 1 1 (quite a feat for the bartender)
- 36 2 1
- 24 3 1
- 18 4 1
- 18 2 2
- 12 6 1
- 12 3 2
- 9 4 2
- 9 8 1
- 8 3 3
- 6 6 2
- 6 4 3
So the bartender tells him where to find the sum of the ages--the man now knows the sum even though we don't. Yet he still insists that there isn't enough info. This must mean that there are two permutations with the same sum; otherwise the man could have easily deduced the ages.
The only pair of permutations with the same sum are 8 3 3 and 6 6 2, which both add up to 14 (the bar's address). Now the bartender mentions his "youngest"--telling us that there is one child who is younger than the other two. This is impossible with 8 3 3--there are two 3 year olds. Therefore the ages of the children are 6, 6, and 2.
Pedants have objected that the problem is insoluble because there could be a youngest between two three year olds (even twins are not born exactly at the same time). However, the word "age" is frequently used to denote the number of years since birth. For example, I am the same age as my wife, even though technically she is a few months older than I am. And using the word "youngest" to mean "of lesser age" is also in keeping with common parlance. So I think the solution is fine as stated.
Saturday, April 18, 2015
Hansel And Gretal
Games Reviewer
7:59 AM
brain
,
hansel and gretal
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
mathematical riddle
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
riddle online
No comments
:
I walk in a straight line in the forest. As I walk, I leave a repeating pattern
of 1's and 0's behind me.
What is the length of the shortest pattern such that if you happen along my trail, you can determine with certainty which direction I was going?
What is the length of the shortest pattern such that if you happen along my trail, you can determine with certainty which direction I was going?
Hansel And Gretal Puzzle Solution
One solution is 010011, and is probably the shortest. In a repeating series of this pattern, we may get:
...11010011010011010011010011...
If we are to look through the sequence, we should find that we
can match the pattern 010011 but not the reverse pattern, 110010. Hence we know
which direction the person was travelling.
...11010011010011010011010011...
Monday, April 13, 2015
TV Show
Games Reviewer
7:57 AM
brain
,
brain teasers
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzle
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
puzzle game
,
show
,
TV
No comments
:

The contestant picked the first door as his guess. At that point, the host walked to the third door and opened it. The door led to no prize, which is something the host knew perfectly well. He then gave the chance to the contestant to switch and pick the second door, if he so wished, or to stick to his first choice and stay with the first door.
Did the contestant have a greater chance of winning the car, by sticking with the 1st door, or by switching to the 2nd door? Or were the chances equal?
Notes:
The contestant knew three things: first, that the host doesn't want him to win; second, that the host was going to open one of the doors; and third, that the host would never open the door picked by the contestant himself... regardless of where the prize really is.
TV Show Puzzle Solution
This puzzle isn't particularly new, but it became very well known in 1990, thanks to the person that allegedly had "the highest IQ ever recorded" -- 228, according to The Guinness Book of WorldRecords. Miss Marilyn vos Savant (yes, it was a female) wrote a solution to this puzzle on her weekly column, published in a popular magazine. This solution led to waves of mathematicians, statisticians, and professors to very heated discussions about the validity of it.The contestant, according to vos Savant, had a greater chance of winning the car by switching his pick to the 2nd door.
She claimed that by sticking to the first choice, the chances of winning were 1 out of 3, while the chances doubled to 2 out of 3 by switching choices. To convince her readers, she invited her readers to imagine 1 million doors instead of just 3. "You pick door number 1," she wrote, "and the host, who knows what's behind every door, and doesn't want you to win, opens all of the other doors, bar number 777,777. You wouldn't think twice about switching doors, right?"
Most of her readership didn't find it as obvious as she thought it was... She started receiving a lot of mail, much of it from mathematicians, who didn't agree at all. They argued that the chances were absolutely equal, whether or not the contestant switched choice.
The week after, she attempted to convince her readers of her reasoning, by creating a table where all 6 possible outcomes were considered:
| Door 1 | Door 2 | Door 3 | Outcome (sticking to door 1) |
| Car | Nothing | Nothing | Victory |
| Nothing | Car | Nothing | Loss |
| Nothing | Nothing | Car | Loss |
| Door 1 | Door 2 | Door 3 | Outcome (switching to other door) |
| Car | Nothing | Nothing | Loss |
| Nothing | Car | Nothing | Victory |
| Nothing | Nothing | Car | Victory |
The table, she explained, shows that "by switching choices you win 2 out of 3 times; on the other hand, by sticking to the first choice, you win only once out of of 3 times".
However, this wasn't enough to silence her critics. Actually, it was getting worse.
"When reality seems to cause such a conflict with good sense," wrote vos Savant, "people are left shaken." This time, she tried a different route. Let's imagine that, after the host shows that there's nothing behind one of the doors, the set becomes the landing pad for a UFO. Out of it comes a little green lady. Without her knowing which door was picked first by the contestant, she is asked to pick one of the remaining closed doors. The chances for her to find the car are 50%. "That's because she doesn't have the advantage enjoyed by the contestant, ie the host's help. If the prize is behind door 2, he will open door 3; if it is behind door 3, he will open door 2. Therefore, if you switch choice, you will win if the prize is behind door 2 or 3. YOU WIN IN EITHER CASES! If you DON'T switch, you'll win only if the car is behind door 1".
Apparently, she was absolutely right, because the mathematicians reluctantly admitted their mistake.
Wednesday, April 8, 2015
The Package
Games Reviewer
7:55 AM
brain
,
logic
,
package
,
play puzzle game
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
puzzles online
No comments
:
G answered his ringing mobile phone. "G here."
"It's H. Do you have the package?"
"Yes. I have the object, in its box."
"Very good," said H. "So send the box to me using the lock I gave you last time we met."
"I'm afraid I can't," said G hestitantly.
"Why not? The locking ring on the box is more than large enough to fit a lock on."
"I seem to have um, misplaced the lock."
"You what!" snarled H. "Do you have any other locks?"
"Yes, but you don't have the keys to them. We can't risk sending an unsecured box, nor an unsecured key. Sending an unlocked lock is out of the question, because they re-lock themselves automatically after a 2 minute timeout."
"Ah, all is not lost... I have an spare lock here... How much time do we have?"
"Plenty," replied G.
"Good. There is a way…

How can they get the box and the object from G to H without any security risk?
"It's H. Do you have the package?"
"Yes. I have the object, in its box."
"Very good," said H. "So send the box to me using the lock I gave you last time we met."
"I'm afraid I can't," said G hestitantly.
"Why not? The locking ring on the box is more than large enough to fit a lock on."
"I seem to have um, misplaced the lock."
"You what!" snarled H. "Do you have any other locks?"
"Yes, but you don't have the keys to them. We can't risk sending an unsecured box, nor an unsecured key. Sending an unlocked lock is out of the question, because they re-lock themselves automatically after a 2 minute timeout."
"Ah, all is not lost... I have an spare lock here... How much time do we have?"
"Plenty," replied G.
"Good. There is a way…

How can they get the box and the object from G to H without any security risk?
Notes:
- They can't meet in person -- that would render the puzzle pointless.
- No, G can't go and look for the misplaced lock!
- You cannot send a key by itself or in an unlocked box.
The Package Puzzle Solution
With the object in the box, G locks it with one of his own locks. He then sends the box to H. H attaches his own lock in addition to G's and then sends it back. G removes his lock and then sends it to H again.Friday, April 3, 2015
Trick Mules
Games Reviewer
7:53 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games online
,
logical puzzles
,
mules
,
play puzzle games
,
puzzle
,
trick
,
trick mules puzzle
No comments
:

Start with the three puzzle pieces arranged so that the two jockeys are correctly riding the two weary-looking mules.
Rearrange the pieces so that the mules miraculously break into a frenzied gallop!
Rearrange the pieces so that the mules miraculously break into a frenzied gallop!
Notes:
The mules do not overlap. There is a clever, but not deceptive solution to this puzzle.
Trick Mules Puzzle Solution
This ambiguous "Trick Mules Puzzle" is solved by the realisation that the mule can have two different orientations. Here the same lines and contours have two interpretations, one horizontal and one vertical.
Sunday, March 29, 2015
Camel Race
Games Reviewer
7:48 AM
brain
,
camel race
,
camel race puzzle
,
camel race riddle
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
puzzle
,
riddle online
No comments
:
The time had come when the father of two sons was to decide who would receive his fortune.
They both kneeled before the aged man as he spoke. "You will both race your camels to the nearest city. The owner of whichever camel arrives at the gates second will receive my fortunes."
Confused, both men rode their camels toward the city, step by step, as slow as they could. As luck would have it, the Great Sage was passing by. Seeing him, they pleaded for his wisdom.
"How might we resolve this such that it doesn't take the rest of our lives," said the first man.
"And yet it must be in a competitive manner," added the second. "Neither of us are willing to concede."
The Great Sage stroked his beard and shared his wisdom.
On hearing his advice, both men ran back to the camels and raced toward the city as fast as they could.

What was the Great Sage's suggestion?
They both kneeled before the aged man as he spoke. "You will both race your camels to the nearest city. The owner of whichever camel arrives at the gates second will receive my fortunes."
Confused, both men rode their camels toward the city, step by step, as slow as they could. As luck would have it, the Great Sage was passing by. Seeing him, they pleaded for his wisdom.
"How might we resolve this such that it doesn't take the rest of our lives," said the first man.
"And yet it must be in a competitive manner," added the second. "Neither of us are willing to concede."
The Great Sage stroked his beard and shared his wisdom.
On hearing his advice, both men ran back to the camels and raced toward the city as fast as they could.

What was the Great Sage's suggestion?
Camel Race Puzzle Solution
The Great Sage told them to swap camels. It is the second camel, not person, to reach the city gates who wins.Tuesday, March 24, 2015
Sherwood Forest
Games Reviewer
7:47 AM
brain
,
brain teasing game
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games online
,
sherwood forest
,
sherwood forest puzzle
No comments
:
"A three-way duel is an old tradition in these lands," said Robin
Hood, "because it is unlikely that between two champions, there
shouldn't come a third party in between, to show he is the bravest.
Miller, Allan-a-Dale, and Brother Tuck now battle like real thieves, and may the best win. Here are the crossbows, each of them with its own set of arrows. The three crossbows are all slightly different, and each set of arrows works only on the crossbow it was designed for. Unfortunately, only one set of arrows is flawless: a quarter of the set of arrows of the second crossbow is faulty, as is an incredible half of the third set. A faulty arrow is indistinguishable from a good one until it is shot. Now, go on, pick a straw, and let fate be fulfilled."
Robin Hood showed his clenched fist, from which three straws stuck out. Miller was the luckiest, having picked the longest straw, while Brother Tuck stared at his short straw with an expression of dread, for he knew full well that none of the three men would miss a target with a good arrow. "Well, Miller, here it is: the king of all crossbows. You have a 100% chance of killing your target. Allan-a-Dale, I hand you the crossbow with a few faulty arrows: with it, your chances are 75%. And there you are, Brother Tuck: the 50% crossbow. But then, a religious man like you could even duel with only your spiritual belief."
The fit monk breathed deep, and muttered, "God almighty, Robin, you want to see me dead. It is not possible to duel in these conditions."
"You are right, Brother Tuck," replied Robin Hood, after thinking for a little while. "Here is what we will do. You, Brother Tuck, will have the right to shoot first, after choosing your desired position on the field. Friends, please remember the rules: you will take position on the corners of an imaginary triangle, each of you 80 yards away from the other two. The order in which you will take turns to shoot is clockwise. On your turn, you may choose which of the other two you wish to shoot. Get ready: it is time to duel!"
Brother Tuck gulped as he chose his position, a taunting raven fluttering overhead squawking songs of doom.
 What position (A or B) did Brother Tuck choose, and which adversary
did he shoot first, in order to have the highest chance of survival?
What position (A or B) did Brother Tuck choose, and which adversary
did he shoot first, in order to have the highest chance of survival?
Miller, Allan-a-Dale, and Brother Tuck now battle like real thieves, and may the best win. Here are the crossbows, each of them with its own set of arrows. The three crossbows are all slightly different, and each set of arrows works only on the crossbow it was designed for. Unfortunately, only one set of arrows is flawless: a quarter of the set of arrows of the second crossbow is faulty, as is an incredible half of the third set. A faulty arrow is indistinguishable from a good one until it is shot. Now, go on, pick a straw, and let fate be fulfilled."
Robin Hood showed his clenched fist, from which three straws stuck out. Miller was the luckiest, having picked the longest straw, while Brother Tuck stared at his short straw with an expression of dread, for he knew full well that none of the three men would miss a target with a good arrow. "Well, Miller, here it is: the king of all crossbows. You have a 100% chance of killing your target. Allan-a-Dale, I hand you the crossbow with a few faulty arrows: with it, your chances are 75%. And there you are, Brother Tuck: the 50% crossbow. But then, a religious man like you could even duel with only your spiritual belief."
The fit monk breathed deep, and muttered, "God almighty, Robin, you want to see me dead. It is not possible to duel in these conditions."
"You are right, Brother Tuck," replied Robin Hood, after thinking for a little while. "Here is what we will do. You, Brother Tuck, will have the right to shoot first, after choosing your desired position on the field. Friends, please remember the rules: you will take position on the corners of an imaginary triangle, each of you 80 yards away from the other two. The order in which you will take turns to shoot is clockwise. On your turn, you may choose which of the other two you wish to shoot. Get ready: it is time to duel!"
Brother Tuck gulped as he chose his position, a taunting raven fluttering overhead squawking songs of doom.

Sherwood Forest Puzzle Solution
Since the order of turns was clockwise, Brother Tuck went to position B, and deliberately missed his firts shot (perhaps he should shoot the raven).Assuming that missing the first shot gives Brother Tuck the best chance that one of the dangerous adversaries gets killed from the other before becoming himself the target (obviously, both Miller and Allan-a-Dale opt to use their first turn to shoot at the most dangerous adversary), it is necessary to consider the chances of shooting from position A and the chances from position B.
By assuming position at A, and missing the first shot (as it is right in the circumstances), Brother Tuck knows that he wouldn't be Miller's target, because Allan-a-Dale is more dangerous. Allan-a-Dale would certainly be killed (Miller's crossbow has 100% chances of hitting the target). At this point, it would again be the monk's turn (with Allan not being in a condition to take his turn), who has a 50% chance of hitting the other survivor, ie Miller, and to therefore end the duel. Obviously, if the religious man misses, then he could only get on his knees and pray, because Miller's next shot would be faultless. So, by choosing position A, Brother Tuck has a 50% chance of survival.
If Brother Tuck chooses position B, and deliberately misses his first shot, the next turn would be Allan-a-Dale's, who would choose the most dangerous adversary, ie Miller. At this point, two different outcomes can happen:
1. Allan misses Miller (25% chances); at this point, Miller will use his turn to shoot Allan. Then it will be Tuck's turn, who will have one chance out of two to pick one of the good arrows (so, it's 50% chances, but it's 50% of 25%, ie 1/8).
2. Allan hits Miller (75% chances); at this point, Brother Tuck will shoot Allan, with 50% chances of success; but this is 50% of 75%, ie 3/8 which, if added to 1/8 of the first outcome, gives Tuck 4/8, ie 50% chances of survival. In case that his shot misses, Tuck would not be a sure victim of Allan's next shot, who might miss with 25% chances. This gives the monk a further 3/32 probabilities (ie 3/4 * 1/2 * 1/4).
The calculation, as shown here, could keep going on and on until the last arrow, and demonstrates that, by choosing position B, Brother Tuck has, besides the 50% chances also offered by position A, a long string of small chances (3/32, 3/256, etc), that are possible if Allan-a-Dale misses at least one (his first, and eventually the next ones) shot at the monk.
Thursday, March 19, 2015
Golf
Games Reviewer
7:40 AM
brain
,
brain teasers
,
golf
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logtical puzzles
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
No comments
:
Jack, Levi, Seth, and Robert were, not necessarily in this order, a
Stock Broker, a Musician, a Doctor, and a Lawyer. They drove, also not
necessarily in order, a Porsche, a Ferrari, a Cadillac, and a Corvette.
The Stock Broker, was remarking to no one in particular one day, while finishing up a round of golf which involved all four friends, that he found it curious that Jack and the Lawyer each wanted to buy the Corvette, but that the Musician didn't because he preferred his Porsche. After the game was over, Seth offered to buy a round of sodas for the Doctor, for the owner of the Cadillac, and for the owner of the Corvette. Levi, who was beaten by the Stock Broker, was in a bad mood, and so he declined Seth's offer and left without joining the others in the club house.
What car did each person own, and what were their respective occupations
The Stock Broker, was remarking to no one in particular one day, while finishing up a round of golf which involved all four friends, that he found it curious that Jack and the Lawyer each wanted to buy the Corvette, but that the Musician didn't because he preferred his Porsche. After the game was over, Seth offered to buy a round of sodas for the Doctor, for the owner of the Cadillac, and for the owner of the Corvette. Levi, who was beaten by the Stock Broker, was in a bad mood, and so he declined Seth's offer and left without joining the others in the club house.
What car did each person own, and what were their respective occupations
Golf Puzzle Solution
The clues given in the puzzle are:- The Stock Broker is not Levi.
- Jack is not the Lawyer; neither Jack nor the Lawyer owns the Corvette.
- The Musician owns the Porsche; therefore no one else owns the Porsche and the Musician owns no other car.
- Seth is not the owner of the Cadillac, the Corvette, nor is he the Doctor; also, the Doctor does not own either the Cadillac or the Corvette either.
- The Doctor, by elimination, must own the Ferrari; the Lawyer must own the Cadillac; the Stock Broker must own the Corvette.
- Tne Stock Broker owns the Corvette. Neither Seth nor Jack own the Corvette, so the Stock Broker must be Robert; since the Stock Broker drives the Corvette, then Robert drives the Corvette.
- The Lawyer owns the Cadillac. Seth does not own the Cadillac; therefore Seth is not the Lawyer; therefore Seth is the Musician; the Musician owns the Porsche; therefore Seth owns the Porsche.
- By elimination, Jack is the Doctor; the Doctor owns the Ferrari; therefore Jack owns the Ferrari.
- By elimination, Levi owns the Cadillac.
- Seth is the Musician and owns the Porsche.
- Levi is the Lawyer and owns the Cadillac.
- Jack is the Doctor and owns the Ferrari.
- Robert is the Stock Broker and owns the Corvette.
Saturday, March 14, 2015
Mountaineer
Games Reviewer
7:37 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
mathematical riddles
,
mountaineer
,
play logical puzzles
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
No comments
:
An Austrian mountaineer left Zurglatt, his village, at eight o'clock
in the morning, and started his climb towards the refuge Tirpitz, on
Gross Glossen mountain. He walked at a steady pace, without stopping,
and his increase in heart pulse rate was negligible. He reached the
refuge at three in the afternoon, i.e. seven hours since he left the
village. At the refuge he rested, admired the view, scribbled some notes
on his diary, sang three lieder, ate two sausages and drank a litre of beer. He then slipped into his sleeping bag and fell asleep.

The next morning, at eight o'clock, he started his descent, again with a steady pace, but faster, since he was travelling downhill. He reached Zurglatt at one in the afternoon, after walking for five hours.
Could there be a point along the path where the mountaineer walked, on the outbound and the return journey, exactly at the same time of day?

The next morning, at eight o'clock, he started his descent, again with a steady pace, but faster, since he was travelling downhill. He reached Zurglatt at one in the afternoon, after walking for five hours.
Could there be a point along the path where the mountaineer walked, on the outbound and the return journey, exactly at the same time of day?
Mountaineer Puzzle Solution
Of course there is. To make sure, imagine two mountaineers: one is in the village, and the other one is at the refuge. They'll both leave at eight o'clock, travel along the same path as our mountaineer, and at his same speed. At some point along the path they'll obviously meet.Monday, March 9, 2015
General Manoeuvres
Games Reviewer
7:35 AM
brain
,
brain teasers
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
manoeuvres
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
puzzle games online
No comments
:
A platoon of 40 soldiers, inclusive of troopers, senior soldiers, sergeants and
commander, was standing by the bank of a river. In order to cross it, they found
only a small rubber rowing boat and a pair of paddles, belonging to two young
boys. Due to its rather restricted size, the boat can only carry either the two
boys together, or a single grown-up.
While the lieutenant - commander of the platoon - was trying to figure out the best way to organize the crossing, the radio received an urgent request: the captain wanted to know exactly how long the platoon would take to cross the river; ie how many minutes, or hours, or days were needed before the last man set his foot on the opposite bank of the river.
The lieutenant worked out that the boat, when carrying the two boys, would take 10 minutes to cross the river. One boy alone on the boat would need 5 minutes. One soldier - soldiers are not the best rowers - would take 8 minutes.
These calculations included the time taken by people to jump on board and get off the boat. After a few seconds, the officer, who had an above average IQ, sent the message with the answer to his captain.
How was the crossing organised, and how long did it take for the entire platoon to cross the river?
While the lieutenant - commander of the platoon - was trying to figure out the best way to organize the crossing, the radio received an urgent request: the captain wanted to know exactly how long the platoon would take to cross the river; ie how many minutes, or hours, or days were needed before the last man set his foot on the opposite bank of the river.
The lieutenant worked out that the boat, when carrying the two boys, would take 10 minutes to cross the river. One boy alone on the boat would need 5 minutes. One soldier - soldiers are not the best rowers - would take 8 minutes.
These calculations included the time taken by people to jump on board and get off the boat. After a few seconds, the officer, who had an above average IQ, sent the message with the answer to his captain.
How was the crossing organised, and how long did it take for the entire platoon to cross the river?
General Manoeuvres Puzzle Solution
The manoeuvre was conducted this way:- The two boys cross to the opposite bank (10 mins)
- One of them stays there while the other comes back (5 mins)
- The boy gets off the boat, a soldier jumps on board and crosses the river
(8 mins)
- The soldier gets off, and the boat returns with the other boy (5 mins)
The total time was therefore [(28 * 40) - 5] = 1115 minutes, which amounts to 18 hours and 35 minutes.
Mike Horan points out that it can be done faster if you leave both boys stranded on one side with the boat on the other. The first 39 soldiers cross at 28 minutes each (1092 minutes). You then have the two boys plus the last solider on one side. The final soldier then rows across himself, hence 1092 + 8 = 1100 minutes.
Wednesday, March 4, 2015
Poker Results
Games Reviewer
7:32 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logica puzzles
,
logical games online
,
play logical puzzle
,
poker
,
poker game puzzle
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
16 comments
:

Person #1 (woman): "Claire is single. The sisters and brothers all together totalled a loss of £9."
Person #2 (man): "My wife and I have lost a total of £1."
Person #3 (woman): "My sisters-in-law, all together, have lost £2."
Person #4 (man): "My brother-in-law and I have managed to lose £12 all together."
Person #5 (woman): "My result combined with that of Alice - who is Daniel's wife and an only child - is overall positive."
How much has each of them won or lost?
Poker Results Puzzle Solution
The 5 people and their wins/losses are:Person #1: Barbara (+ £4).
Person #2: Edward (- £5).
Person #3: Alice (+ £14).
Person #4: Daniel (- £7).
Person #5: Claire (- £6).
This result is obtained from the statements of the 5 people.
- Since the sisters-in-law (#1 and #5) lost, wile #5 and Alice have won, then
#3 is Alice.
- Alice won £14, because £2 lost by the sister-in-law, and £12 lost by the
men.
- #1 is Barbara, as she talks about Claire.
- Alice is the only child, therefore the sisters-in-law must be sisters of
the husband (Daniel).
- Daniel lost £7, as the bunch of brothers and sisters have lost a total of
£9, of which only £2 was lost by the sisters.
- Edward lost £5, as the two men lost a total of £12, of which £7 was lost
by Daniel.
- Barbara - Edward's wife because Claire is single - won £4, as the total
lost by the couple Barbara-Edward is £1.
- Claire lost £6, as the total loss of the two sisters is £2, but Barbara won £4.
Friday, February 27, 2015
Snake
Games Reviewer
7:30 AM
brain
,
brain teasers
,
logic
,
mathematical games
,
mathematical puzzles
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
snake
No comments
:
How are we to seat them within our only 8 remaining spaces?"
frowned the manager of the theatre. Everyone was well aware of the
problems of these eight people. They came as a group, but each person
loathed one or two of the other people and could not stand to be near
them.
The assistant manager gestured to the plan of seats remaining. "I have made eight counters to represent each of the people in this group. I have numbered them logically. Person 1 and 8 only hate 2 and 7 respectively. All the others hate the numbers on either side of them." He rubbed his chin in thought, "the only problem is how can we arrange them so that no-one is right next to anyone they hate?"

Place the counters 1 to 8 in the grey squares above such that no two consecutive counters are adjacent to one another horizontally, vertically nor diagonally.
The assistant manager gestured to the plan of seats remaining. "I have made eight counters to represent each of the people in this group. I have numbered them logically. Person 1 and 8 only hate 2 and 7 respectively. All the others hate the numbers on either side of them." He rubbed his chin in thought, "the only problem is how can we arrange them so that no-one is right next to anyone they hate?"

Place the counters 1 to 8 in the grey squares above such that no two consecutive counters are adjacent to one another horizontally, vertically nor diagonally.
Snake Puzzle Solution
Counters 1 and 8 need to be in the middle since they each have only one number that they cannot be neighbours with. Hence 7 and 2 must go in the sidewings, and the rest is trivial.| 3 | 5 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 8 | 2 |
| 4 | 6 |
Sunday, February 22, 2015
Triangular Paradox
Games Reviewer
7:23 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzles
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
triangular paradox
,
triangular paradox puzzle
No comments
:
Consider the diagram below. Figure 1 shows four shapes. The same
four shapes have been rearranged in Figure 2. However, there is now a gap, but
none of the shapes have changed.
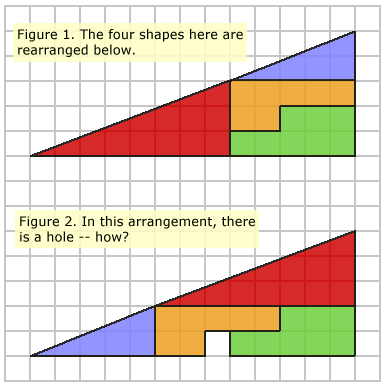 How can this be?
How can this be?

Triangular Paradox Puzzle Solution
You will have tried to calculate the areas of everything involved. The red triangle has an area of 12 squares, the blue triangle has 5 squares, the orange shape has 7, and the green shape has 8. The sum of all these parts is 12 + 5 + 7 + 8 = 32 squares.You might have thought that the large, enclosing figure was (5 × 13) / 2 = 32.5, and wondered how there is a 0.5 square discrepency.
However, this is not the case. The enclosing figures are not actually a triangles at all: the blue triangle has a gradient of 2 / 5 = 0.4, and the red triangle has a gradient of 3 / 8 = 0.375. The thick black lines aid in deceiving the eye into seeing the 'hypotenuse' as a straight line.

OK, so it's a bit of a trick. But you may note that I never said those big "triangles" were actually triangles!
Tuesday, February 17, 2015
Job Interview
Games Reviewer
7:16 AM
2 ropes puzzle
,
brain
,
job interview
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzles
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
No comments
:
"Come in," welcomed the interviewer.
The nervous interviewee, Tom, entered the the office, glancing back at the remaining interviewees sitting stiffly on their chairs.
"My name is Patrick," said the interviewer as he shut the door. Patrick was an elderly man with a slight stoop and a squinty eye, perhaps caused by the wearing of the monocle that now hung from his jacket pocket. "Sit down," gestured Patrick as he himself took a seat. The manner in which he spoke was somewhat strange; he seemed to group his sentences into groups of six words or so.
As Tom seated himself, he noticed that Patrick gave off a slight smell of something he could not quite identify at this moment.
"Alright," stated Patrick in his funny voice. "You must answer this question. There are two ropes. Each is one metre long. You have some matches. Each rope burns in one hour. The ropes do not burn linearly. That is, half the rope does not necessarily burn in half an hour. How do you measure out forty-five minutes?"
Tom thought for a while, and then smiled, even as that squinty eye stared hard.
Using only the matches and the two ropes, how can you measure out 45 minutes?
The nervous interviewee, Tom, entered the the office, glancing back at the remaining interviewees sitting stiffly on their chairs.
"My name is Patrick," said the interviewer as he shut the door. Patrick was an elderly man with a slight stoop and a squinty eye, perhaps caused by the wearing of the monocle that now hung from his jacket pocket. "Sit down," gestured Patrick as he himself took a seat. The manner in which he spoke was somewhat strange; he seemed to group his sentences into groups of six words or so.
As Tom seated himself, he noticed that Patrick gave off a slight smell of something he could not quite identify at this moment.
"Alright," stated Patrick in his funny voice. "You must answer this question. There are two ropes. Each is one metre long. You have some matches. Each rope burns in one hour. The ropes do not burn linearly. That is, half the rope does not necessarily burn in half an hour. How do you measure out forty-five minutes?"
Tom thought for a while, and then smiled, even as that squinty eye stared hard.
Using only the matches and the two ropes, how can you measure out 45 minutes?
Job Interview Puzzle Solution
"You set light to both ends of the rope 1 and just one end of rope 2. It will take half an hour for the two burning ends of rope 1 to meet. Then you set light to the remaining end of rope 2. The time it will take for rope 2 to finish burning will be a further 15 minutes. Hence all together, both ropes burned in this manner will take 45 minutes to burn." Tom leaned back in his chair and folded his arms.That squinty eye stared at him some more. "Very well," stated Patrick after some time. "We will let you know about the success of your application shortly." He stood and shook Tom's hand.
As Tom left the room, he grinned again. "Elderberries," he muttered to himself.
Thursday, February 12, 2015
Napoleon's Star
Games Reviewer
7:14 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzles
,
mathematical riddles
,
napoleon
,
napoleon star puzzle
,
puzzle
,
puzzles online
,
star
No comments
:
Napoleon had an obsession: a star. His star. He would talk about it to
everyone, and whoever would listen to him out of respect, would point at the star
in the sky. Napoleon even talked about the star during the Russian campaign, while
his troops were receding.
It seems like Talleyrand sent him the game - Napoleon's Star - on the evening of 17th June, 1815, the day before the Battle of Waterloo. It has been said that the great general spent the entire night and the following day, until sunset, trying to solve the game, without hearing the noise of the battle and without listening to his officers pleading for help. When he came out of his tent to breath some fresh air, looking tired and unshaven, but with the solution in his grasp, Waterloo had already been won by the English, and his troops were fleeing with no order or hope.

Here's the game: start from any of the ten points, marked with a letter, and follow - in a staight line - to the third point from the starting position (eg from a to g); place a coin on this third point. Then pick another point unoccupied by any coin, and again go to a third unoccupied point in a straight line (a coin on the second point doesn't matter), and place a coin on it. Repeat the procedure until you've placed nine coins.
It seems like Talleyrand sent him the game - Napoleon's Star - on the evening of 17th June, 1815, the day before the Battle of Waterloo. It has been said that the great general spent the entire night and the following day, until sunset, trying to solve the game, without hearing the noise of the battle and without listening to his officers pleading for help. When he came out of his tent to breath some fresh air, looking tired and unshaven, but with the solution in his grasp, Waterloo had already been won by the English, and his troops were fleeing with no order or hope.

Here's the game: start from any of the ten points, marked with a letter, and follow - in a staight line - to the third point from the starting position (eg from a to g); place a coin on this third point. Then pick another point unoccupied by any coin, and again go to a third unoccupied point in a straight line (a coin on the second point doesn't matter), and place a coin on it. Repeat the procedure until you've placed nine coins.
Napoleon's Star Puzzle Solution
To be able to place nine coins, it is necessary to make the 3rd point of each step equal to the start point of the previous step. For example:a-g; i-a; c-i; f-c; e-f; h-e; b-h; j-b; d-j.

With such a simple solution, it's hard to believe that Napoleon stayed in charge for so long.
Saturday, February 7, 2015
Southern Cross
Games Reviewer
7:08 AM
brain
,
logic
,
logical games
,
logical puzzles
,
mathematical puzzles
,
number puzzles
,
numers riddles
,
puzzle
,
southern cross
No comments
:
There is a missing number in the table below.
What number goes in the blank box?
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | 52 | 63 | 94 | 46 |
What number goes in the blank box?
Southern Cross Puzzle Solution
The missing number is 18. The numbers in the bottom row are the square of the numbers in the top row, but with their digits reversed.| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | 52 | 63 | 94 | 46 | 18 |
Monday, February 2, 2015
Bread And Water
Games Reviewer
7:05 AM
brain
,
bread
,
bread and water puzzle
,
logic
,
logic puzzles
,
logical arcade
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
water
No comments
:

He collapsed, looked up and thought that the sun had had the better of even his eyes; he saw two bedouins walking towards him. Mirages, he thought. He shook his head and rubbed his eyes to clear it, but the bedouins were still there, getting closer. When they reached him, Alek weakly asked for water and some food, and promised he would repay them generously.
They introduced themselves as Azad and Mohammed. "Water," one of them said, "is free." As far as food was concerned, they would share with him, which consisted of bread only. Azad had three slices, and Mohammed had five. They put the slices together, split them in three equal parts, and each of them ate his portion quietly. When they finished their meal, Alek pulled out his eight golden coins, and set them before the bedouins, telling them to share them fairly. He thanked them for saving his life, promised to call them sometime, and with renewed energy continued his journey.
When the traveller was gone, the two bedouins looked at the eight golden coins for a little while, and then Mohammed moved his hand to grab five coins.
"Hold it there!" said Azad. "We will share them as good friends; four coins each!"
Mohammed was convinced he deserved five coins, but Azad would not agree, and the argument grew louder. Before the first punch was thrown, the Great Sage happened to be passing by on his camel. He enquired about the matter, which was quickly explained by the bedouins.
"Neither 5 - 3 nor 4 - 4 are fair," stated the Great Sage, before sharing his wisdom.
The bedouins got their fair share of the coins, and the Great Sage went on his way, satisfied that yet another problem had been resolved.
How much did each of the bedouins get?
Bread And Water Puzzle Solution
Each slice of bread was divided into 3 equal pieces, making a total of 24 pieces. These were then divided between the three men, 8 pieces each.Mohammed had 5 slices, and so contributed 15 pieces. He ate 8 pieces himself, so 7 were eaten by Alek.
Azad had 3 slices, which contributed 9 pieces. Azad ate 8, leaving 1 piece for Alek.
Therefore, Mohammed gave 7 pieces of bread away, and Azad only gave 1 piece. So Mohammed deserves 7 gold coins and Azad only 1. If he were smarter or less greedy, Azad should have accepted Mohammed's initial offer of 5 - 3.
Wednesday, January 28, 2015
Canopus
Games Reviewer
7:03 AM
brain
,
canopus
,
logic
,
logical games
,
mathematical puzzles
,
numbers puzzle
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
No comments
:
There is a number made of eleven tens of thousands, eleven thousands, eleven hundreds, and eleven units?
What is that number?
What is that number?
Canopus Puzzle Solution
A nice and simple sum does the trick.…| 110,000 | + |
| 11,000 | + |
| 1,100 | + |
| 11 | = |
__________
|
|
| 122,111 | |
Friday, January 23, 2015
Deneb
Games Reviewer
7:00 AM
brain
,
deneb
,
geometrical puzzle
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
play logical games
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games online
No comments
:
She was an absent minded one, forever seeing things that interest her
intellilect and hold her in thought for hours on end. On this particular
time, she saw a curious symbol, her mental processes setting
formulating a problem to solve.

Starting at any point, how can you draw the whole symbol by tracing along the lines and never tracing along the same line twice?

Starting at any point, how can you draw the whole symbol by tracing along the lines and never tracing along the same line twice?
Deneb Puzzle Solution

Sunday, January 18, 2015
Visit At The White House
Games Reviewer
6:52 AM
brain
,
brain teasers
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
play puzzles
,
puzzle
,
riddle online
,
white house
,
white house riddle
No comments
:
"This," started the guide, "is the Buttons Room."
The Druggar of Bongo Ghango - the chief of a large country by the River Ghango - looked around. "It's a nice room, but where are the buttons? The only ones I see are, ahem, the ones on your shirt."
"Your Highness. The buttons, which could start a nuclear armageddon in a matter of seconds, are there, behind that panel," replied the guide, while pointing at a large panel at the end of the room.
"How can that be??? Why? Anybody - a madman, for example - could come here and press those terrible buttons?"
"Your Highness, it is very safe actually: for every button there is a slot, where a magnetic card must be inserted to activate the corresponding button. No card, no button. To launch the missiles, all buttons must be activated and pressed, and only a handful of people have the magnetic cards, and each card contains a different code from all the other ones."
"But it's the same thing! Any of these persons could go completely ballistic and start a nuclear war."
"In that case, the only dangerous man is the President of the United States, as he is the only person that holds all the codes, which would allow him to press all the buttons. The other people that hold some codes are the Vice-President of the United States, the President of the Senate, the Secretary of State, the Chief of the Armed Forces, and the Dean of Harvard University. Each of these gentlemen holds an incomplete set of magnetic cards, and the distribution of the codes is such that, if the President of the United States is not available, the entire set of buttons can be activated by the Vice-President, together with anyone of the other four men. If both the President and the Vice-President of the United States are unavailable, the buttons can still be activated by any three of the other four men. Therefore, to launch the missiles, it is needed either the President, or the Vice-President plus anyone of the other four men, or any three of the other four men."
"What if someone tried to press randomly many buttons, one after the other?" asked the Chief.
"Nothing would happen with the missiles, but the room would fill up with a narcotic gas, and an alarm would alert the guards and the CIA."
"So, how many buttons are there, and how are they distributed between the Vice-President and the other four personalities?"
And that's the question we'll ask the reader: what is the minimum number of buttons, and how are they distributed?
The Druggar of Bongo Ghango - the chief of a large country by the River Ghango - looked around. "It's a nice room, but where are the buttons? The only ones I see are, ahem, the ones on your shirt."
"Your Highness. The buttons, which could start a nuclear armageddon in a matter of seconds, are there, behind that panel," replied the guide, while pointing at a large panel at the end of the room.
"How can that be??? Why? Anybody - a madman, for example - could come here and press those terrible buttons?"
"Your Highness, it is very safe actually: for every button there is a slot, where a magnetic card must be inserted to activate the corresponding button. No card, no button. To launch the missiles, all buttons must be activated and pressed, and only a handful of people have the magnetic cards, and each card contains a different code from all the other ones."
"But it's the same thing! Any of these persons could go completely ballistic and start a nuclear war."
"In that case, the only dangerous man is the President of the United States, as he is the only person that holds all the codes, which would allow him to press all the buttons. The other people that hold some codes are the Vice-President of the United States, the President of the Senate, the Secretary of State, the Chief of the Armed Forces, and the Dean of Harvard University. Each of these gentlemen holds an incomplete set of magnetic cards, and the distribution of the codes is such that, if the President of the United States is not available, the entire set of buttons can be activated by the Vice-President, together with anyone of the other four men. If both the President and the Vice-President of the United States are unavailable, the buttons can still be activated by any three of the other four men. Therefore, to launch the missiles, it is needed either the President, or the Vice-President plus anyone of the other four men, or any three of the other four men."
"What if someone tried to press randomly many buttons, one after the other?" asked the Chief.
"Nothing would happen with the missiles, but the room would fill up with a narcotic gas, and an alarm would alert the guards and the CIA."
"So, how many buttons are there, and how are they distributed between the Vice-President and the other four personalities?"
And that's the question we'll ask the reader: what is the minimum number of buttons, and how are they distributed?
Visit At The White House Puzzle Solution
There are 7 buttons. The magnetic cards, as held by the six persons,
and marked with an X, are distributed as follows:
| Person | Buttons | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| President | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Vice President | X | X | X | X | X | X | - |
| President of Senate | X | X | X | - | - | - | X |
| Secretary of State | X | - | - | X | X | - | X |
| Chief of Armed Forces | - | X | - | X | - | X | X |
| Dean of Harvard | - | - | X | - | X | X | X |
Tuesday, January 13, 2015
Visit At The Kremlin
Games Reviewer
6:50 AM
brain
,
brain teasing games
,
kremlin
,
logic
,
logic puzzles
,
logical games
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
,
riddles online
No comments
:
"This," explained Colonel Nevskij to the Druggar of Bongo
Ghango - chief of a large country by River Ghango - "is the Buttons Room."
"I've seen a room like this in Washington," replied the big Chief, smiling with satisfaction, "there too, you couldn't see a single button. The only ones I can see here are, uh.. hehe, the ones on your uniform, Colonel!"
"Ahah, comrade Druggar likes joking. But the buttons are here," replied the Soviet, pointing at a large panel at the end of the room, "they are behind that panel."
"A very large panel," observed the Chief, "much larger than the one at the White House: I presume there are more buttons here."
"Of course, comrade Druggar: in America, only a bunch of opportunistic capitalists has a saying in the big decisions, while here, uh, here is different: the entire Soviet community, through its representatives, takes part in the decision process of the Union."
"Any citizen could then come here and press the buttons?"
"Err, no, not exactly. If I tried to do it, the room would fill up with narcotic gas, an alarm would set off, and... Well, no need to talk about that. For each button there is a slot, into which a magnetic card must be inserted, to activate the corresponding button. Therefore, no card, no button. To launch the missiles, every button must be activated and pressed, and only a handful of comrades holds the magnetic cards, which of course, each of them has a different code from the others. The personalities holding the cards are the Secretary of the Communist Party, the President of the Praesidium, the Chief of the KGB, and five comrades, Heroes of the Soviet Union. The distribution - and here is the originality of our system - is such that the Secretary of the Party holds the complete set of codes, and so he can launch the missiles by himself; if the Secretary is not available, the missiles can be launched by the President of the Praesidium together with the Chief of the KGB, or by anyone of these two, together with any two of the five Heroes of the Union. If - Marx forbid - the Secretary, the President, and the Chief have all been victimised by an imperialistic attack, our nuclear response can be initiated by any four of the five Heroes of the Soviet Union; any four of them would be sufficient to have the entire set of magnetic cards to activate the buttons."
"So, how many buttons are there?" asked the Chief.
What is the minimum number of buttons, and how are they distributed?
"I've seen a room like this in Washington," replied the big Chief, smiling with satisfaction, "there too, you couldn't see a single button. The only ones I can see here are, uh.. hehe, the ones on your uniform, Colonel!"
"Ahah, comrade Druggar likes joking. But the buttons are here," replied the Soviet, pointing at a large panel at the end of the room, "they are behind that panel."
"A very large panel," observed the Chief, "much larger than the one at the White House: I presume there are more buttons here."
"Of course, comrade Druggar: in America, only a bunch of opportunistic capitalists has a saying in the big decisions, while here, uh, here is different: the entire Soviet community, through its representatives, takes part in the decision process of the Union."
"Any citizen could then come here and press the buttons?"
"Err, no, not exactly. If I tried to do it, the room would fill up with narcotic gas, an alarm would set off, and... Well, no need to talk about that. For each button there is a slot, into which a magnetic card must be inserted, to activate the corresponding button. Therefore, no card, no button. To launch the missiles, every button must be activated and pressed, and only a handful of comrades holds the magnetic cards, which of course, each of them has a different code from the others. The personalities holding the cards are the Secretary of the Communist Party, the President of the Praesidium, the Chief of the KGB, and five comrades, Heroes of the Soviet Union. The distribution - and here is the originality of our system - is such that the Secretary of the Party holds the complete set of codes, and so he can launch the missiles by himself; if the Secretary is not available, the missiles can be launched by the President of the Praesidium together with the Chief of the KGB, or by anyone of these two, together with any two of the five Heroes of the Union. If - Marx forbid - the Secretary, the President, and the Chief have all been victimised by an imperialistic attack, our nuclear response can be initiated by any four of the five Heroes of the Soviet Union; any four of them would be sufficient to have the entire set of magnetic cards to activate the buttons."
"So, how many buttons are there?" asked the Chief.
What is the minimum number of buttons, and how are they distributed?
Visit At The Kremlin Puzzle Solution
There are 20 buttons. This is because there are 10 combinations of Heroes in pairs of 2, and this is multiplied by 2 because these combinations have to be mapped to two different persons (the President of the Praesidium or the Chief of KGB). The magnetic cards, as held by the eight persons, and marked with an X, are distributed as follows:| Person | Buttons | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secretary of Party | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| President of Praesidium | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chief of KGB | - | - | - | - | - | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 1st Hero | X | X | X | X | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | - |
| 2nd Hero | X | X | X | - | X | X | X | X | - | - | - | - | - | - | X | X | X | X | - | X |
| 3rd Hero | X | X | - | X | X | - | - | X | - | X | X | - | - | X | - | X | X | - | X | X |
| 4th Hero | X | - | X | X | X | - | X | - | X | - | X | - | X | - | - | X | - | X | X | X |
| 5th Hero | - | X | X | X | X | X | - | - | X | X | - | X | - | - | - | - | X | X | X | X |
Thursday, January 8, 2015
Frogs
Games Reviewer
6:48 AM
brain
,
frogs
,
frogs puzzle
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
play logical games
,
play puzzles online
,
puzzle
No comments
:

Amanda:
"I am a frog but I look like a princess."
"There are at least three frogs between the four of us."
Barbara:
"I'm a princess."
"Corinna always lies."
Corinna:
"There is only one frog here."
"I'm a frog that looks like a princess."
Deborah:
"Two of us are frogs."
"I'm a princess."
Are there any frogs? If so, what are their names
Frogs Puzzle Solution
The only frog is Amanda. The table below shows, on the left, all possible combinations of frogs (X stands for frog, - stands for non-frog), while on the right pane there is the control of the truthfullness (T for true, F for false) of each given statement, for each combination of frog population. The only combination where every girl tells one true statement and one false one, is the emphasised row. Hence, there's only one frog, and that's Amanda.| Possible Frogs | Statement | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | ||||
| - | - | - | - | F | F | T | F | F | F | F | T |
| - | - | - | X | F | F | T | F | T | F | F | F |
| - | - | X | - | F | F | T | F | T | T | F | T |
| - | - | X | X | F | F | T | T | F | T | T | F |
| - | X | - | - | F | F | F | F | T | F | F | T |
| - | X | - | X | F | F | F | F | F | F | T | F |
| - | X | X | - | F | F | F | T | F | T | T | T |
| - | X | X | X | F | T | F | T | F | T | F | F |
| X | - | - | - | T | F | T | F | T | F | F | T |
| X | - | - | X | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | F |
| X | - | X | - | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T |
| X | - | X | X | T | T | T | T | F | T | F | F |
| X | X | - | - | T | F | F | F | F | F | T | T |
| X | X | - | X | T | T | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| X | X | X | - | T | T | F | T | F | T | F | T |
| X | X | X | X | T | T | F | T | F | T | F | F |
Tuesday, January 6, 2015
Creative Lamps
Games Reviewer
8:05 AM
creative design
,
creative lamps
,
designers ideas
,
digital art
,
lams design
,
light design
,
modern art
,
modern design
,
modern lamps
,
play puzzle games
,
puzzles
No comments
:
These unusual and very interesting lamps are developed by the Studio Cheha (Tel Aviv, Israel) and they all share one interesting secret which is not immediately visible. See the full post and find out!
The thing is that they are all flat, though it may seem otherwise. Look at them once again and discover that these objects are 2-dimensiona!:)
The thing is that they are all flat, though it may seem otherwise. Look at them once again and discover that these objects are 2-dimensiona!:)
Saturday, January 3, 2015
Swapping Art
Games Reviewer
6:46 AM
art
,
brain
,
logic
,
logical puzzles
,
max ernst
,
max ernst art
,
puzzle
,
puzzle games
,
riddles online
,
swapping
No comments
:
"Four drawings by Max Ernst are worth as much as five sketches by Magritte,
do you agree?" asked Giorgio Parconi, an Italian art dealer. He was tired
of arguing over this.
"D'accord!" agreed Cesar Blanchard, who was the director of a Parisian art gallery.
"And we all agree that two sketches by Magritte plus one drawing by Ernst are worth as much as two paintings by Bacon. Right?"
"Bon," nodded the frenchman.
"So, I'm offering you four drawings by Ernst plus one sketch by Magritte, and in return you give me three sketches by Magritte and two paintings by Bacon. It's perfectly fair, isn't it?"
Blanchard remained silent, he had the feeling that something was wrong.
Was the Italian dealer offering a fair swap?
"D'accord!" agreed Cesar Blanchard, who was the director of a Parisian art gallery.
"And we all agree that two sketches by Magritte plus one drawing by Ernst are worth as much as two paintings by Bacon. Right?"
"Bon," nodded the frenchman.
"So, I'm offering you four drawings by Ernst plus one sketch by Magritte, and in return you give me three sketches by Magritte and two paintings by Bacon. It's perfectly fair, isn't it?"
Blanchard remained silent, he had the feeling that something was wrong.
Was the Italian dealer offering a fair swap?
Swapping Art Puzzle Solution
The swap is unfair. If we abbreviate with an E the drawings by Ernst, an M for Magritte's sketches, and a B for Bacon's paintings, we can rewrite the equations as stated by the Italian dealer as:- EEEE = MMMMM (both dealers agreed on this)
- MME = BB (again, both dealers agreed on this too)
- MMMBB = EEEEM (the French dealer wasn't sure of this)
The problem gives us 3 equations:
1. 4x = 5y
2. 2y + x = 2z
3. 3y + 2z = 4x + y
Equation 2. can be rewritten as:
4. x = -2y + 2z
Equation 3. can be rewritten as:
5. 4x = 2y + 2z
Adding equations 4. and 5. gives us:
6. 5x = 4z
Combining 1. and 6., we get:
7. 4x = 5y = (16/5)z
If we convert the offer (3.) in terms of y, we get:
8. 3y + 2(25/16)y = 5y + y
ie 3y + (25/8)y = 6y
ie 6.125y = 6y
The last equation is not absolutely true, which proves the swap is unfair.
Subscribe to:
Posts
(
Atom
)














